
Solar Eclipses for 2014, 2015


What is a Solar Eclipse
Solar Eclipses occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth and directly blocks the light of the sun. Because the moon is located between the Sun and Earth the dark side of the moon is facing Earth and is in a New Moon phase. Like a Lunar Eclipse there are a few different types of Solar Eclipse depending on the moon's position.
When is the next Solar Eclipse
The next Solar Eclipse will occur on April 29th, 2014. It will be visible in Indian, Australia, Antarctica.
This Solar Eclipse Calendar is a listing of all Solar Eclipses from 2013 to 2015. The cart shows the date of each eclipse as well as the time and type of Eclipse.
Also have a look at the
Full Moon & New Moon Calendar
| 2014 Solar Eclipses |
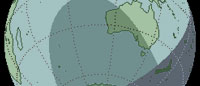
Apr 29, 2014 |
Annular - Will be visible in Indian, Australia, Antarctica. TD of Greatest Eclipse - 06:04:32 UT |
 |
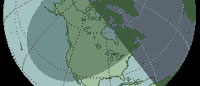
Oct 23, 2014 |
Partial - Will be visible in Northern Pacific and North America. TD of Greatest Eclipse - 21:45:39 UT |
 |
| 2015 Solar Eclipses |
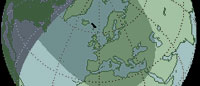
Mar 20, 2015 |
Total Eclipse - Will be visible in Iceland, Europe, North Africa and Northern Asia TD of Greatest Eclipse - 09:46:47 UT |
 |
Sept 13, 2015 |
Partial Eclipse - South Africa, South Indian and Antarctica. TD of Greatest Eclipse - 06:55:19 UT |
 |
Solar Eclipse Terms
Total Eclipse - A solar eclipse in which the Moon's umbral shadow traverses Earth (Moon is close enough to Earth to completely cover the Sun). During the maximum phase of a total eclipse, the Sun's disk is completely blocked Moon. The Sun's faint corona is then safely revealed to the naked eye.
Hybrid Eclipse - A solar eclipse in which the Moon's umbral and antumbral shadows traverse Earth (the eclipse appears annular and total along different sections of its path). Hybrid eclipses are also known as annular-total eclipses. In most cases, hybrid eclipses begin as annular, transform into total, and then revert back to annular before the end of their track. In rare instances, a hybrid eclipse may begin annular and end total, or vice versa.
Partial Eclipse - A solar eclipse in which the Moon's penumbral shadow traverses Earth (umbral and antumbral shadows completely miss Earth). During a partial eclipse, the Moon appears to block part (but not all) of the Sun's disk. From the prospective of an individual observer, a partial eclipse is one in which the observer is within the penumbral shadow but outside the path of the umbral or antumbral shadows.
Annular Eclipse - A solar eclipse in which the Moon's antumbral shadow traverses Earth (the Moon is too far from Earth to completely cover the Sun). During the maximum phase of an annular eclipse, the Sun appears as a blindingly bright ring surrounding the Moon.
Greatest Eclipse - The time in the Eclipse when the the Moon's shadow axis is closest to the Earth's center.
Terrestrial Dynamical of Greatest Eclipse - The excact time when the axis of the Moon's shadow cone passes closest to Earth's center.
Eclipse magnitude - The fraction of the Sun's diameter obscured by the Moon. For annular eclipses, the eclipse magnitude is always less than 1. For total eclipses, the eclipse magnitude is always greater than or equal to 1. For both annular and total eclipses, the value listed is actually the ratio of diameters between the Moon and the Sun.
Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA's GSFC
For more information on Solar Eclipse and tons of data, visit the Nasa Solar Eclipse Page.
